Saunders-Roe/Westland Aircraft/British Hovercraft Corporation
SR-N1 - SR-N2- SR-N3 - SR-N4 - SR-N5 - SR-N6 - BH-7 - BH-8 - Hover Freighter - AP1-88
Sam Saunders started work in the family boatbuilding business on the River Thames in the late 1870's.
In 1901 Sam moved his own business building boats to the Isle of Wight. Always looking for innovations and willing to build 'what the customer wanted', S.E. Saunders formed an Aircraft Department in 1909 and was involved in early British aviation, especially in sea planes and flying boats.
In 1929, the company SE Saunders was renamed 'Saunders-Roe' when A.V. Roe took a financial interest in the company. Through to the mid 1950's Saunders-Roe was mainly involved with high speed launches and Flying Boats.
In 1958, the National Research and Development Corporation awarded Saunders-Roe a contract to build the first full sized hovercraft - the SR-N1 (Saunders-Roe - Nautical One). On the 11th June 1959, the SR-N1 was launched and, only 5 weeks later, the SR-N1 became the first hovercraft to cross the English Channel from Calais to Dover.
Under 'guidance' from the Government, the late 1950's was a time of reorganisation of the UK aircraft industry, this led to Westland Aircraft Ltd taking over the Saunders-Roe hovercraft interests in July 1959.
Cecil Hugh Latimer-Needham was the person who had the idea of using a skirt to keep the air cushion under the vehicle. In October 1961, Latimer-Needham sold his skirt patents to Westland Aircraft.
 Pathe1966 video clip from Hovershow '66 with SR-N3, SR-N5 & SR-N6
Pathe1966 video clip from Hovershow '66 with SR-N3, SR-N5 & SR-N6
Over the next 6 years, the Saunders-Roe Division of Westland Aircraft designed (or at least proposed) the majority of their future craft, the exception being the AP1-88 which was a joint BHC, NRDC and Hovertravel development started in 1981.
Picture right - BHC's Columbine Works with Red Funnel car ferry and Hovermarine HM2 sidewall hovercraft. (picture supplied by Barry Sowerby).
On 1st March 1966 the Westland's and Vickers' hovercraft activities were merged to form the British Hovercraft Corporation (shareholdings - Westland Aircraft 65%, Vickers 25%, National Research and Development Corporation 10%).
In October 1970, Westland Aircraft bought out both of the other partners and BHC became a wholly owned part of the Westland group.
In 1971, BHC acquired Cushioncraft Ltd (of St. Helens) from financially troubled Britten-Norman Ltd., none of the Cushioncraft designed were developed further.
As well as developing and manufacturing hovercraft, over the years BHC became increasingly involved with supplying the world-wide Aerospace industry with composite components.
1984 saw the name 'British Hovercraft Corporation' changed to Westland Aerospace as the nature of the business had changed with hovercraft being a very small part.
Subsequent changes in the company names etc. are of little interest regarding the history of hovercraft as the company had effectively exited hovercraft development/manufacture.
(Click on an image to get a larger version)
| SR-N1 | |
 |
Launched 11th June 1959 |
The SR-N1 in its original configuration - saucer shape, obvious air clearance and no jet engine behind the central air intake. Short YouTube video clip of SR-N1 post modification Original spec:
Pathe 1959 video clip of SR-N1 including cross channel trip |
|
| SR-N2 | |
 |
Launched January 1962 SRN2 Hovercraft travelling at speed (Postcard) |
YouTube video clip of SR-N2 with side damage |
|
| SR-N2A | |
 |
A civilian version of the SR-N3 concept - in fact production of the SR-N3 started without the company having a contract, if the contract had not been forthcoming, the craft could well have been completed as a SR-N2A, |
| SR-N3 | |

 |
SR-N3 Military hovercraft shown left at Hovershow '66 - 18th June 1966 (CC4 in foreground) Launched 9th December 1963, delivered to IHTU at HMS Daedalus, June 1964 |
The Interservice Hovercraft Trials Unit (IHTU), based at HMS Daedalus near Gosport (where the Hovercraft Museum is located), used the SR-N3 and numerous subsequent hovercraft to evaluate them for military use. |
|
| SR-N4 (Mountbatten) | |

above - first hover 5th December 1967 - note the original, 'lower' skirt line 
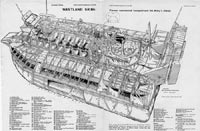
Early cutaway diagram  Hoverlloyd SR-N4 Mk 1 at speed |
First time on the cushion - 5th December 1967
Mk 1 configuration - as originally built and supplied to Seaspeed and Hoverlloyd for cross channel routes:
Mk 2 configuration - modified by BHC for Hoverlloyd by rearranging internal division of craft - 1st delivered January 1973
|
Pathe 1967 video clip of SR-N4 after roll-out Mk 3 configuration - modified by BHC for Seaspeed by stretching - 1st one delivered 6th April 1978
YouTube video clip of 2 SR-N4 Mk 3's at Dover.
|
|
| SR-N5 (Warden) | |

 |
Launched 11th April 1964
Left, lower - at West Cowes with Red Funnel car ferry behind |
| Pathe 1966 video of SR-N5 Fire Engine | |
| SR-N6 (Winchester) | |
|
Launched 1964 Basically a stretched SR-N5 Shown here at Hovershow '66 - 18th June 1966 - SR-N6 with SR-N5 and SR-N3 behind
|
|
See also SR-N6 hovercraft in operation - Pathe 1970 video clip of SR-N6 in Africa |
|
| SR-N6 Mk1S | |
 (pictures contributed by Geoff Weatherhead) (pictures contributed by Geoff Weatherhead) |
Over
the winter 1971/72, both Seaspeed SR-N6 hovercraft had more powerful Gnome engines (1000 shp) fitted and were streched by 10ft to give increased seating for 58 passengers, these were known as the Mk1S. The first of these took to the water from BHC, East Cowes on 11th February 1972. |
| The picture above shows the Sea Hawk Mk1S SR-N6 in July 1975 passing in front of the BHC hanger (before the Union Flag was painted on the doors). | |
| SR-N6 Mk 6 | |
 |
The Mk6 was 3 metres longer than the standard SR-N6 and had seating for 55 passengers.
It offered greater manoeuvrability and lower noise due to the use of two 10ft dia propulsion propellers. A modified skirt and more power engine (1125 hp Rolls Royce marine Gnome gas turbine) were also fitted. |
| YouTube video clip of SRN6 Mk6 departing the beach at Hovershow '09 | |
| BH-7 (Wellington) | |
 |
Launched 31st October 1969
Shown below with front loading ramp |
  |
|
 |
|
| YouTube video clip of BH-7 on exercise with Belgian navy | |
| BH-7 hulls in Cowes harbour and on the BHC East Cowes slipway | |

 |
|
| BH-8 | |
 |
Model of 80 ton BH-8 at Hovershow '66 - concept only
|
| Hover Freighter | |
 |
BHC concept from 1970 for a 4,000 ton "hoverfreighter" - 'maximum speed over calm water ... 50kts (92km/hr), maximum range of about 500 Nm (920km)' |
| AP1-88 | |
|
|
The AP1-88 was a joint BHC, National Research Development Council (NRDC) and Hovertravel development started in 1981. It was a step away from the 'aircraft' style design and manufacture used on all previous craft from BHC. The welded aluminium hull was produced by a Gosport boat builder outside of the aircraft manufacturing environment of BHC and was fitted out at the Duver Works of Hoverwork. Prototype launched July 1982. In addition to passenger versions, cargo versions were built (see left). |
YouTube video clip of AP1-88 leaving Southsea
As well as the AP1-88's built by BHC, at least 3 craft were built under licence by NQEA Australia Pty Ltd, the first order for these was received in February 1986. |
|