Hovercraft Development Ltd / National Physical Laboratory Hovercraft Group
Hovercraft Development Ltd was established in 1959 by the National Research Development Corporation (NRDC) to develop and exploit the early hovercraft patents. HDL had a facility at Hythe on Southampton Water where the HD-1 and HD-2 development craft were developed.
The HD-1 was of mainly wooden construction and was built by ship builders J. Samuel White of Cowes, Isle of Wight - the craft was described as the first non-amphibious craft with air curtains at both the front and rear (or bow and stern for the nautically minded!). Built as a full scaled test bed for skirts and control.
Pathe 1965 video clip of HD-1 and other Hovercraft Development projects.
The HD-2 was produced as a full sized test vehicle to research hovercraft controls.
In October 1967, the development and research aspects of HDL were transferred to the National Physical Laboratory to form the NPL Hovercraft Group. HDL continued with the licensing of the hovercraft patents.
The Hythe site continued until the mid 1970's.
(Click on an image to get a larger version)
| HD-1 | |
 |
Shown here at Hovershow '66 - 18th June 1966, the HD-1 was designed by HDL and built by J. Samuel White shipbuilders of Cowes, Isle of Wight the craft was first launched from Hythe (Southampton Water) on 22 October 1963. Originally the craft was a non-amphibious, sidewall craft, subsequently the sidewalls were removed and it was given a full skirt. |
Pathe 1965 video clip of HD-1 |
|
| [top] | |
| HD-2 | |


|
Designed and constructed (1966) by HDL's own staff.
The HD-2 is now in the Hovercraft Museum in a very sad state (2008) |
| HD-2 hovercraft on the slipway at Hythe contributed by Roy Johnson, TechnicalScientific.com | |
| Pathe 1968 video clip of hovercraft tests including HD-2 | |
| [top] | |
| HU-4 | |
 |
Originally the Cushioncraft CC4, this was acquired by NPL for research into low pressure fan propulsion systems (amongst other things) and was renamed HU-4.
|
See the Cushioncraft page for details of the craft in its original configuration. |
|
 |
Rear view of HU-4 |
| [top] | |
| Hover- bed | |
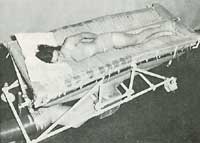 |
HDL's Hoverbed Developed by HDL in 1966/67, the hoverbed was designed to treat patients suffering from burns, the idea was that sterilised air supporting the patient rather than linen would speed recovery. |
| [top] | |
|
Tracked Hovercraft From the early days of hovercraft, the use of the technology for tracked trains was considered. Much research was done world-wide (especially in France where a full size track was established).
|
|
 |
 |
| Left: Early concept model of tracked Hovercraft Right: An experimental Tracked Hovercraft rig at Hythe (1960's) Pathe video clip of the rig in action (1963) World-wide the hovertrain technology seems to have been overtaken by MagLev (magnetic levitation). |
|


 A
full size research vehicle - the RTV31 (Research Test Vehicle 31) - and a test track at Erith in Cambridgeshire were built in the
early 1970's and the vehicle achieved speeds in excess of 100 mph from a standing start over 1 mile. The vehicle used linear motors
for propulsion along the track it sat on. Funding for the project was withdrawn by the Tory Government in February 1973 and development
stopped. The RTV31 vehicle is now located at the entrance to
A
full size research vehicle - the RTV31 (Research Test Vehicle 31) - and a test track at Erith in Cambridgeshire were built in the
early 1970's and the vehicle achieved speeds in excess of 100 mph from a standing start over 1 mile. The vehicle used linear motors
for propulsion along the track it sat on. Funding for the project was withdrawn by the Tory Government in February 1973 and development
stopped. The RTV31 vehicle is now located at the entrance to